Demystifying Motorcycle Jargon: A Guide to Common Technical Definitions
Introduction:
Motorcycles, with their sleek aesthetics and strong motors, have long had an air of mystery about them. Understanding the technical features of motorcycles, on the other hand, might be scary, particularly for novices. In this blog, we will deconstruct the most popular technical definitions related with motorbikes, making it easier for both fans and novices to comprehend these fascinating machines.
In order to view this blog in a simple web story format, Click this link https://stories.site/shreyzcorner/bike-technical-terms/
1. Ground Clearance:
Ground clearance is the distance between the lowest point of a motorbike (typically the chassis or exhaust) and the ground. It influences the ability to ride on uneven terrain without harming the bike. A higher ground clearance is preferred for off-road riding, while a lower clearance improves stability on paved roads.
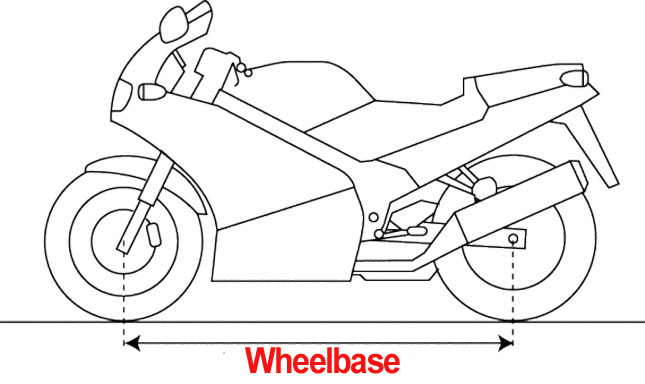
2. Wheelbase:
The wheelbase is the distance between the front and rear wheel centres. It has an impact on the stability and maneuverability of the motorcycle. A longer wheelbase improves stability at high speeds, whereas a shorter wheelbase improves agility for tight bends.
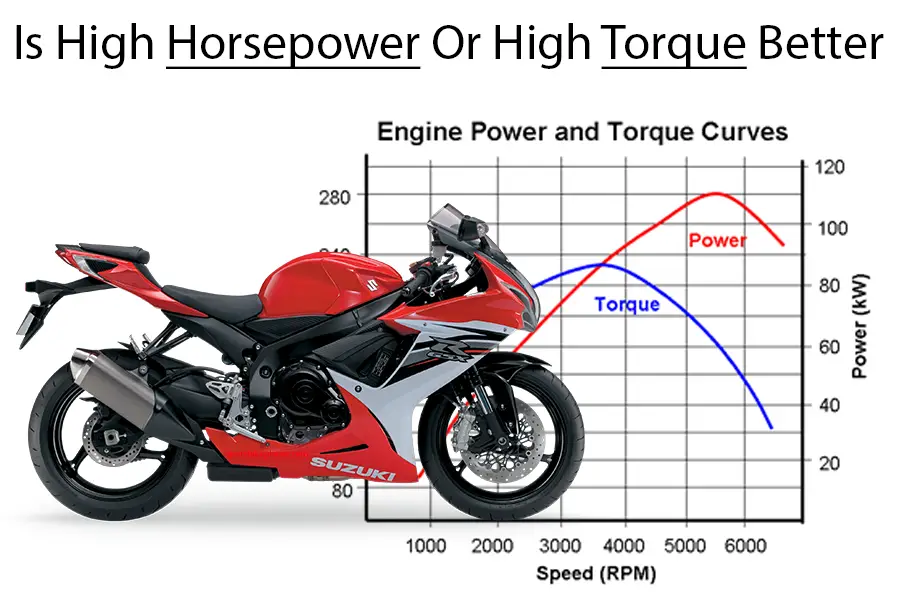
3. Power and Torque:
Image Courtesy:https://www.sportbikeplanet.com/horsepower-or-torque-motorcycle/,https://scenic.app/motorcycle-torque-vs-horsepower-how-standardised-are-manufacturer-reported-numbers/
Power and torque are critical performance measures for bikes. The pace of work is represented by power, which is measured in horsepower (HP) or kilowatts (kW). Torque, which is usually measured in Newton-meters (Nm) or pound-feet (lb-ft), determines the engine's rotating force or pulling power. Higher power and torque ratings often result in faster acceleration and top speed.
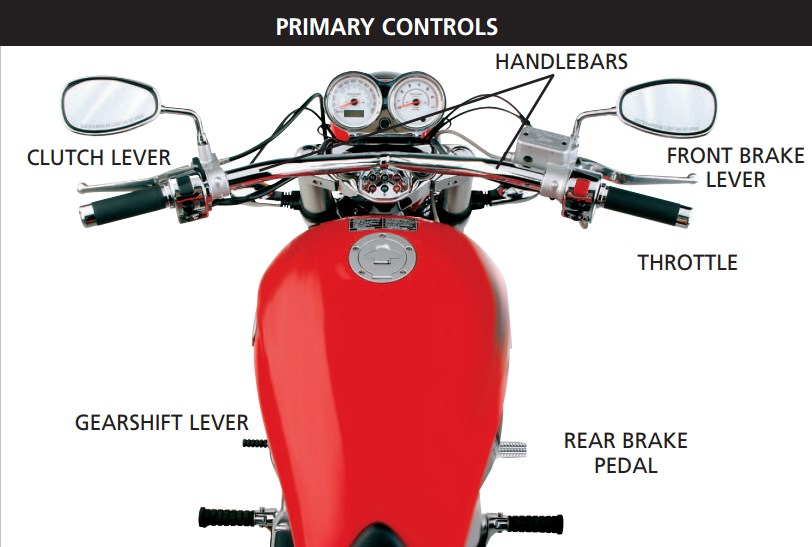
4.Brake System:
The brake system is critical to the safety of a motorbike. It is usually made up of disc or drum brakes. Callipers and rotors are used in disc brakes to provide improved stopping power and heat dissipation. Drum brakes, on the other hand, work by pressing shoes against a rotating drum. Understanding the different types of brake systems and how to maintain them is critical for safe riding.
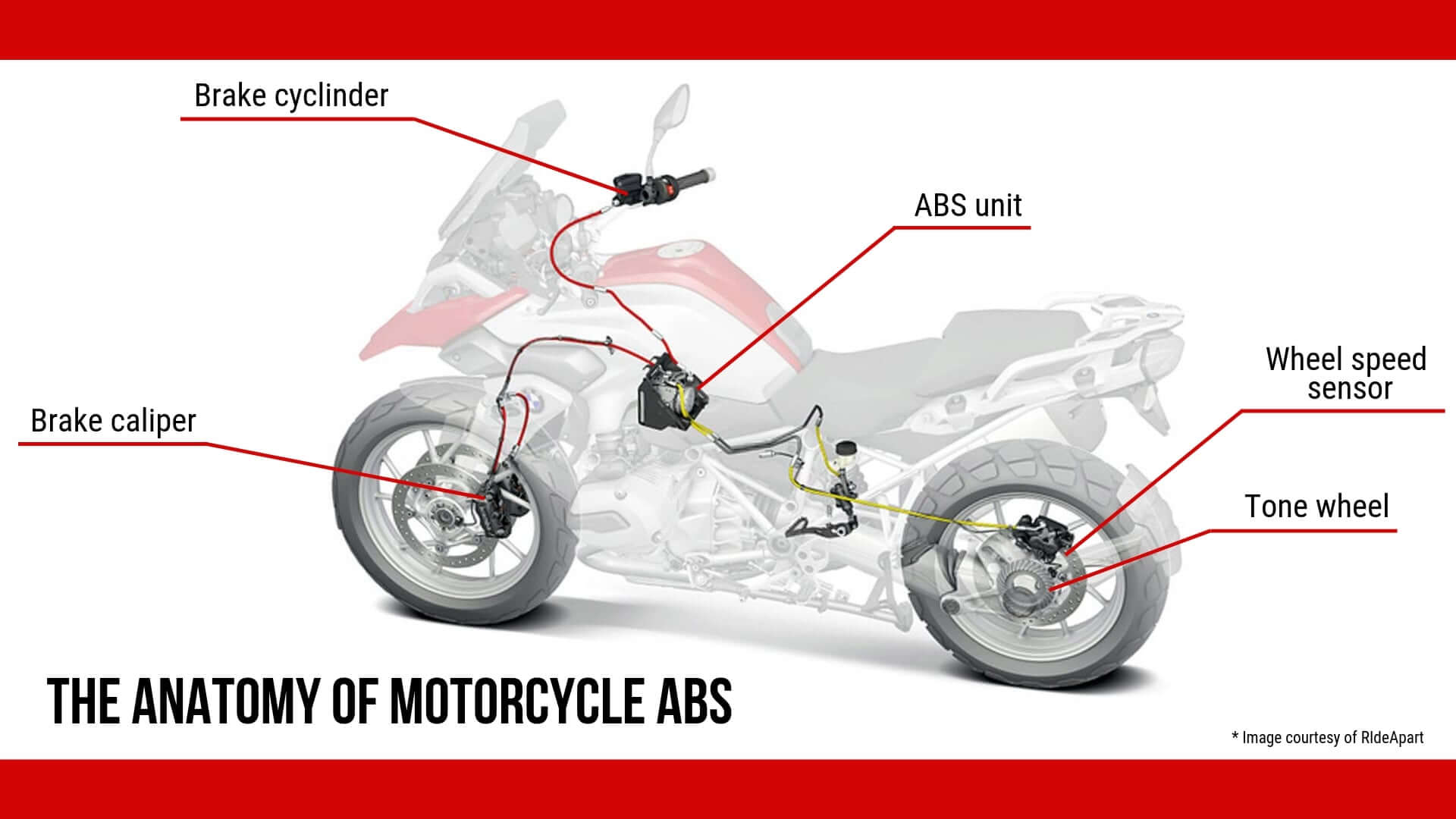
5. ABS (Anti-lock Braking System):
Image courtesy:https://www.motorcyclelegalfoundation.com/motorcycle-abs/
ABS is a safety device that keeps the wheels from locking up when braking hard, lowering the chance of skidding or losing control. It automatically regulates the brake pressure, allowing the rider to maintain steering control. ABS is especially useful in emergency situations or when travelling on slick surfaces.
6.Clutch:
The clutch engages or disengages engine power from the gearbox, allowing the rider to smoothly shift gears. It gives the rider control over power delivery and gear changes. Understanding clutch operation and understanding clutch control are critical for smooth acceleration and effective gear shifting.
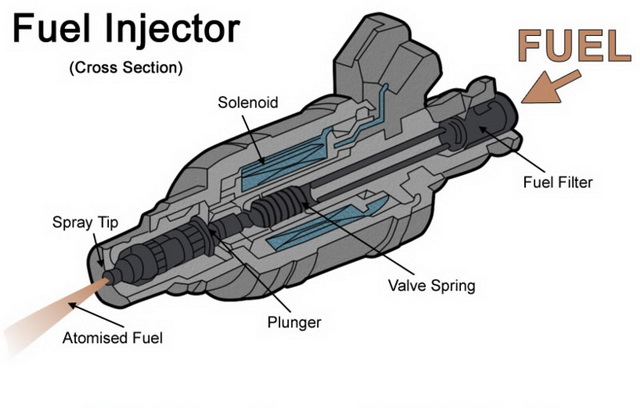
7. Fuel Injection:
Image courtesy:https://www.bikesrepublic.com/featured/fuel-injection-what-is-it/
Fuel injection is a modern method of supplying fuel to engines. It is designed to replace traditional carburetors and improve fuel efficiency, throttle response, and pollution control. Fuel injection systems carefully measure the amount of fuel injected into the engine, optimising performance over a wide range of riding circumstances.
Conclusion:
We can demystify the world of motorbikes and obtain a better grasp of these fantastic machines by being familiar with these basic technical definitions. From ground clearance to fuel injection, every detail influences a motorcycle's performance and safety. Whether you're a seasoned rider or a curious newcomer, understanding these terminology will help you make informed decisions and appreciate the engineering marvels that motorbikes truly are.
Dear readers I appreciate you taking the time to go through my blog. Your participation and encouragement are greatly appreciated by me. I appreciate the chance to discuss my ideas with you. Keep checking back for more intriguing material soon!




Comments
Post a Comment